Our work on how alterations of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis affect in cancer published in Nature Cancer
We are very happy to have published one of the first articles of the Nature Cancer journal.
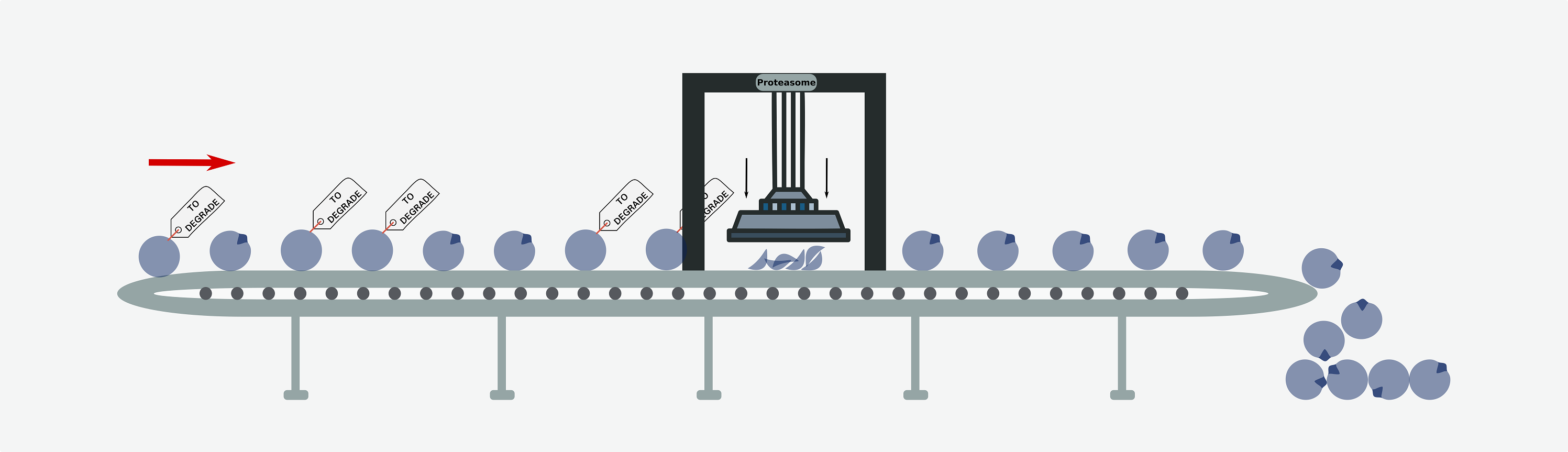
We have systematically analyzed how alterations in the ubiquitin proteolysis system contribute to tumorigenesis. Our results reveal that several oncogenes are frequently targeted by mutations that affect the sequence of their degrons or their cognate E3 ubiquitin ligases, causing an abnormal increase in their protein abundance. Overall, we found that approximately one in ten driver mutations interferes with UPS either by affecting a protein degron or by altering the E3 that labels it for degradation.


