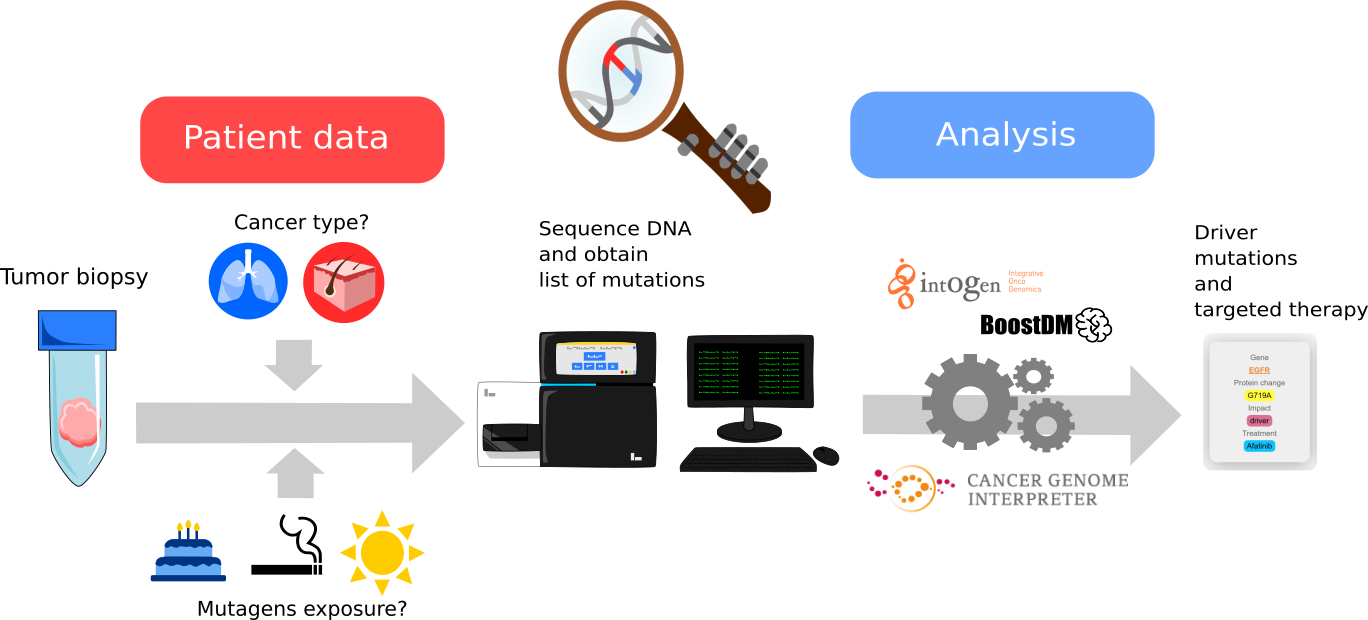
A sample has arrived to the lab! Can you help the Cancer Detective?
You are about to start a simulation where you will analyze a tumour sample from an imaginary cancer patient.
Follow these steps:
1. Select relevant data from this patient and annotate it into the system
2. Sequence the tumour DNA to identify its somatic mutations
3. Launch our computational tools to identify driver mutations and targeted therapies
4. Analyze the results
Check the introduction and the resources to learn more about cancer genomics.